Obstructive Sleep Apnoea
Picture this.
.You fall asleep…… Muscles relax…… Airway passages narrow and / or collapse, making breathing difficult or impossible…
Loud snoring, snorts, pauses in airflow, followed by labored breathing…
Oxygen level begins to fall…… 33% SpO2
You continue to struggle for breath… time goes by…… 10 seconds… 20… … 40 seconds between breaths… and longer…
Heart rate falls below normal… there is decreased oxygen to pump through the body… brain senses low oxygen / high carbon dioxide level… releases a jolt of adrenaline – ‘Fight or Flight’ response to awaken the brain and body and to prevent suffocation….
Heart rate speeds up in response to the rush of adrenaline…
You awaken briefly, take five or six breaths, breathing in oxygen and blowing off excess carbon dioxide, then often reposition on the bed.
You typically do not remember arousal, oxygen / carbon dioxide levels return to near normal, brain allows you to resume sleeping.
This cycle repeats throughout the night. Some people who suffer from apnoea experience these chocking episodes 100 times per hour.
Snoring: The Not-So-Silent Killer
Ranging from a gentle rumble to a raging snorting cacophony, the sounds of snoring disturb millions of households every night.Snoring is extremely common. About 25% of all men snore every night; about half as many women snore.
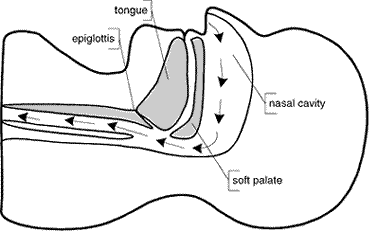
Unusual among young people, the prevalence of snoring increases beyond age 35. Snoring is a noise produced when an individual breathes during sleep, causing soft palate to vibrate.
In addition to so–called “simple snoring”, there is a medical condition – a potentially serious one – called ‘sleep apnoea’.
In sleep apnoea, a sleep disorder suffered by about 10 % of middle-aged adults and 40% of severe snorers, the upper airway becomes completely obstructed for 10 seconds or longer, and often many times – sometimes 100 times during the night.
Although a serious life threatening medical disorder, more than 80% of sleep apnoeics fail to understand the problem or get medical help for it.
Studies have revealed that obstructive sleep apnoea increases your risk of hypertension, coronary heart failure, and stroke, not to mention the inherent risk of the sleep deprivation it causes.
SLEEP APNOEA:
Sleep apnoea is a condition where, for a variety of reasons, a person ceases to breathe during sleep (for 10 seconds or more).
Hypopnoea is a reduction of airflow during sleep.
Types of sleep apnoea:
1. Obstructive sleep apnea
2. Central sleep apnea
3. Mixed sleep apnea
OBSTRUCTIVE SLEEP APNOEA: Defined as having no airflow or a significant decrease in airflow although there are continuing respiratory efforts.
CENTRAL SLEEP APNOEA: Defined as the absence of both airflow and breathing efforts. In essence, it is the failure of the brain to signal the diaphragm and other muscles of ventilation to contract.
MIXED SLEEP APNOEA: As the name implies this is simply a combination of both central and obstructive sleep apneas. It generally begins as a central apnea followed by an obstructive component.
OBSTRUCTIVE SLEEP APNOEA (OSA):
- The most common and severe form of sleep apnoea.
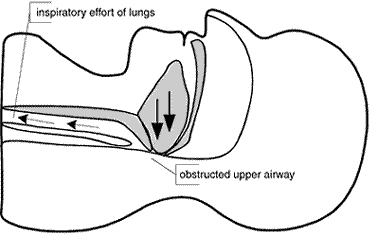
- The muscules of the soft palate and tongue relax and lose their ability to hold the airway open against the negative pressure generated by inhalation. The airway collapses, causing an interruption of breathing.
Obstructed Upper Airway
 OSA - CAUSES:
OSA - CAUSES:Factors causing sleep apnea can be divided into two main components,
STRUCTURAL
- Decreased hypoglossal muscle tone allowing the tongue to fall back and obstruct the airway.
- Malformations of the jaw or oropharynx.
- Excess facial and neck tissue due to obesity
- Abnormally narrow airway due to tumors, growths, etc
- Substances such as alcohol and sleeping pills increase the frequency and length of breathing pauses.
- Much less common than osa.
- In this form of apnoea, the airway may stay open, but the diaphragm and chest muscles stop working, causing cessation of breathing.
- Snoring is not associated with this form of sleep apnoea.
- Central apnoea becomes more common as people grow older, and perhaps one in four people age 60 or older experience disturbed breathing during sleep.
- It becomes more frequent and severe in people who have congestive heart failure or neurological disorders.